Introduction
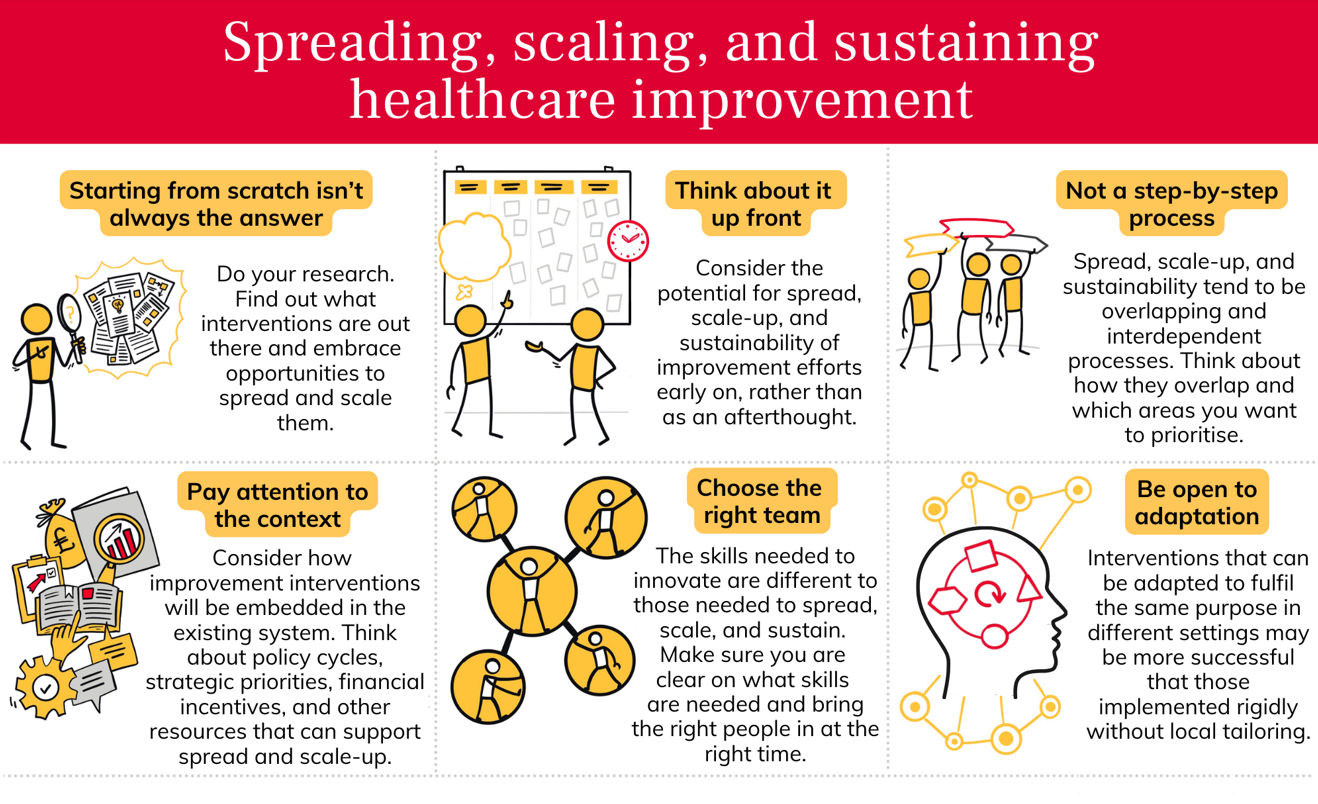
This resource offers clear, practical guidance on the key concepts of spread, scale-up, and sustainability in healthcare improvement. It defines these terms, explains how they overlap, and introduces useful frameworks to help teams successfully implement and maintain improvements. The resource also includes practical questions to guide planning, alongside links to further reading for deeper insights. Whether you’re starting a new improvement initiative or looking to expand and sustain existing work, this guide provides actionable advice to support your efforts.
Definitions
There’s no shortage of information out there on this topic, but the way the terms ‘spread’, ‘scale-up’, and ‘sustainability’ are used can be confusing. So, let’s start with some definitions.
Spread
(sometimes referred to as adoption or adoption and spread)
The term ‘spread’ refers to taking improvement interventions that have been successful in one setting and implementing them somewhere else. This can be done with or without modifying the original intervention. The original setting doesn’t have to be within healthcare – you can take ideas and inspiration from other industries such as hospitality for improving team culture or the transport industry for scheduling.
Scale-up
Scale-up involves developing the infrastructure needed to enable widespread implementation of improvement interventions. Think about the broad range of infrastructure and process needed to successfully scale-up the intervention. It might include technology, systems, behaviour, people, culture, and leadership.
Sustainability
Sustainability refers to improvement interventions being maintained over time, so that new ways of working and improved outcomes become the norm.
Spread, scale-up, and sustainability do not happen in a neat, linear process. They tend to be overlapping and interdependent processes.
Practical frameworks
There are lots of frameworks that can be used to support spread, scale-up, and sustainability. Here are three that may help you in a practical, actionable way.
The Dynamic Sustainability Framework
This framework has three main parts:
- Intervention: Specific components like clinical guidelines, delivered by certain people (e.g. clinicians) using methods like in-person meetings to achieve desired outcomes.
- Implementation context: Characterised by human resources, organisational and technical infrastructure, and learning and supervision approaches.
- Ecological system: Includes other clinical settings, legislative and regulatory environment, market influences, and population characteristics.
Key principles:
- Tailoring interventions to their specific context enhances sustainability
- Optimizing interventions in their intended context helps keep stakeholders engaged and learning throughout the process
- Using progress measures for feedback allows for adaptation and continuous learning
Examples of potential use
- Managing complex care
- Achieving a clinical standard
- Implementing new changes to guidelines
Practical frameworks
NASSS framework (non-adoption, abandonment, and challenges to scale-up, spread, and sustainability)
The NASSS framework aims to:
- inform the design of technology
- support planning for implementation, spread, or scale-up
- help identify innovations where increased complexity may limit success
- increase learning by explaining failures.
It has seven domains that vary in complexity (simple, complicated, or complex):
- nature of the health condition or illness
- type of technology or intervention
- value proposition
- role of intended adopters
- organisational capacity and support structures
- complexity of the wider system
- potential for continuous embedding and adaptation over time.
Programmes with multiple complex domains may need significant effort to become sustained.
Examples of potential use
Technology projects, including video consultations, remote monitoring, and decision support.
Practical frameworks
The 3S Scale-Up Infrastructure Approach
This approach differentiates between internal and external contexts that influence improvement.
It suggests three infrastructural components are needed to support large-scale implementation:
- Structure: teams and individuals with capacity and accountability to deliver scale-up, supported by a reporting process.
- Strategy: A clear plan for scaling with specific actions, milestones, and assigned responsibilities.
- Support: Reliable data monitoring systems for regular reviews, and expertise in adaptive facilitation for scale-up.
It Includes a practical checklist to rate each component’s presence in the intervention setting. Low scores can highlight areas needing attention to improve the chance of scale-up success.
Examples of potential use
Creating and sustaining an enabling infrastructure and environment for any improvement intervention.
Useful resources
THIS Institute | Chrysanthi Papoutsi, Trisha Greenhalgh, and Sonja Marjanovic
Approaches to Spread, Scale-Up, and Sustainability
https://www.cambridge.org/core/elements/approaches-to-spread-scaleup-and-sustainability/B2A69BE3D579E3BDB5922340CE23D617
The Health Foundation
The spread challenge
https://www.health.org.uk/publications/the-spread-challenge
The Health Foundation
Using communications approaches to spread improvement
https://www.health.org.uk/publications/using-communications-approaches-to-spread-improvement
The Health Foundation
Communications in health care improvement – a toolkit
https://www.health.org.uk/publications/communications-in-health-care-improvement-a-toolkit
Institute for Healthcare Improvement
The Breakthrough Series: IHI’s Collaborative Model for Achieving Breakthrough Improvement
https://www.ihi.org/resources/white-papers/breakthrough-series-ihis-collaborative-model-achieving-breakthrough
Institute for Healthcare Improvement
Human Learning Systems
https://www.humanlearning.systems/
Nuffield Trust
Achieving scale and spread: Learning for innovators and policy-makers
https://www.nuffieldtrust.org.uk/research/achieving-scale-and-spread-learning-for-innovators-and-policy-makers
Innovation Unit and the Health Foundation
Against the odds: Successfully scaling innovation in the NHS. A joint report from the Innovation Unit and the Health Foundation
https://www.health.org.uk/publications/against-the-odds-successfully-scaling-innovation-in-the-nhs
World Health Organization
Practical guidance for scaling up health service innovations
https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/44180
Practical questions
Asking the right questions early on can help shape a clear and effective approach to spread, scale-up, and sustainability.
Overarching
- What are your long term aims and ambitions for the work?
- Do you want to see this work spread to other settings? If so, how do you see this happening?
- Dissemination of learning through academic/professional routes?
- Creating dedicated resources for people to use to ‘self-serve’ their
own adoption process?
- Working closely with early adopters to further test the model?
- Creating an infrastructure that will allow widespread implementation and scale-up?
- A combination of some or all of these approaches over time?
- How could you build decision-making about spread, scale up, and/or sustainability into your programme management and engagement approaches from the beginning? Literature review? Market research?
Spread
- How will you identify settings most likely to adopt or spread this work?
- When engaging with potential early adopters:
- How will you identify their needs and offer them support?
- How might this change your approach or leadership?
- How will you encourage them to share their learning to improve your intervention?
- What is ‘core’ to your work and what can be ‘adapted’ to suit the local context?
- What time, resources, and funding will you need and how long for?
- What is your theory of change for spread?
- What leadership skills are needed and how do they differ from the original work?
- What is your communication and engagement plan?
- What risk management strategies can you put in place to minimise challenges?
- How do you plan to measure, evaluate, and share learning?
- How will you plan for a successful ending of your involvement?
Scale-up
- What kind of central infrastructure and processes will be required to achieve widespread implementation and scale of your work?
- If you do need infrastructure, what funding, time, and resources will be required and for how long?
- How will you organise and lead this infrastructure? What’s your strategy?
- What are your core measures for success?
- How will you aim to reduce unwarranted variation across adopting sites?
- How will you share learning and best practice across all of the sites involved?
- What happens when the supporting infrastructure ends? How will you transition this work to business as usual?
- How will you share the results of the scale-up?
Sustainability
- How will you identify what a sustainable change looks like in practice?
- How will you focus on sustainability by continuously adapting the improvement within the context, and the broader system?
- What will you measure from the start of your work that will support you to build a long-term business case? What data will you collect?
- How will you maintain fidelity to the intervention/process and consistently review and agree any changes?
- What will you measure long-term to improve your chances of sustainability?
- What leadership behaviours are needed to ensure that any cultural, social, and behavioural norms that are required alongside any technical changes are thought about and integrated into the approach?
- Who are your local champions and stakeholders? What do they need to sustain this work?
Acknowledgements
This resource was produced in collaboration with NHS England South West, Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, and North Bristol NHS Trust. It is adapted from ‘Approaches to Spread, Scale-Up, and Sustainability’, by Chrysanthi Papoutsi, Trisha Greenhalgh, and Sonja Marjanovic; part of THIS Institute’s series ‘Elements of Improving Quality and Safety in Healthcare’.
Download the resource
This resource is available to download for free. We hope that you find it useful in your work.
If you would like to order printed copies, or talk to us about adding your organisation’s logo to the resource, please email enquiries@thisinstitute.cam.ac.uk with the subject Explain THIS.